In the realms of Digital Audio Transmission, HDMI and S/PDIF TOSLINK Optical Cables are the two dominating cables. There is one more cable to transmit Digital Audio in the form of a Coaxial Cable. In this definitive guide on Coaxial Speaker Cable, we will talk in detail about Digital Coaxial Cables. We will see the physical and electrical characteristics of a typical Coaxial Cable. After that, we will see different types of Coaxial Cables. Coming to the audio side of things, we will take a look at the pros and cons of using a Coaxial Speaker Cable instead of HDMI or Optical Cables for digital audio transmission. We will also try to bust some myths surrounding coaxial cables, their usage with subwoofers, etc.
A Brief Note on Coaxial Cable
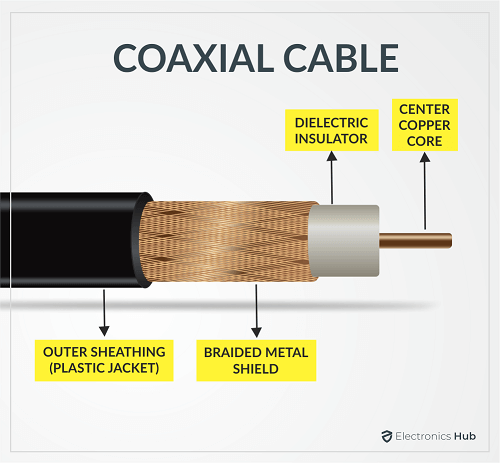
The Coaxial Cable or sometimes Coax Cable is one of the oldest transmission mediums in the field of communication. You might have used a coaxial cable before for cable TV or broadband internet from your cable company. Physically, there are four layers of a typical coaxial cable. In the center, there is a solid copper wire that acts as the main conductor to transmit data. Surrounding this is thick insulation, usually made up of PVC or Teflon materials. The surface of the dielectric insulator is covered with a braided metal foil, usually made up of copper but sometimes Aluminum as well. These woven metal layers act as the second conductor (for the return path or ground) and also as a shield to the main copper conductor. There is a huge significance to the metallic shield as it helps in reducing the amount of external interference. On top of the metal shield, there will be an outer cover made up of plastic. The plastic cover is also known as a Plastic Sheath or Jacket. Now that we have seen the structure of a typical Coaxial Cable, what exactly is the use of this cable? In its basic form, the Coaxial Cable is a type of RF Transmission Line that can high-frequency and high-speed data for long distances. As a result, one of the main applications of Coaxial Cables is the transmission of cable TV signals from your operator to your home. If you have a satellite dish on your rooftop, then you have to use a coaxial cable between the antenna and the receiver inside your home.
Different Types Of Coaxial Cables
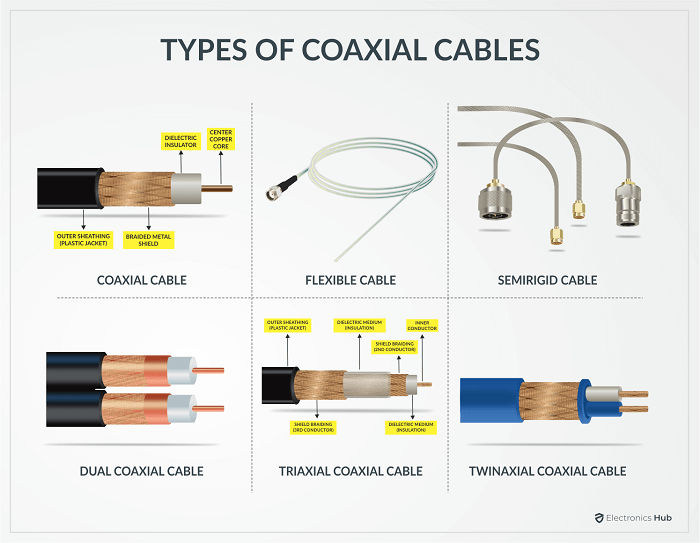
Let us now take a look at different types of Coaxial Cables. We can categorize coaxial cables based on their characteristic impedance, construction, and RG Standards.
Based on Characteristic Impedance
The Characteristic Impedance is an important parameter of a Transmission Line. When it comes to coaxial cables, we have the standard 50 Ω and 75 Ω impedance cables. Apart from these two, we also have 52 Ω and 93 Ω, which are somewhat rare. Then, we have the “high-power” 30 Ω Coax Cable. Most of the medical appliances such as CAT Scanners, X-Ray Machines, MRI Machines, etc. use these 30 Ω coaxial cables.
1. 50 Ω Coaxial Cable
This is a lower-impedance coaxial cable that is suitable for high-frequency digital transmissions such as ethernet. Another popular application of 50 Ω coaxial cable is the link cable between the Radio Transmitters and their Antennas.
2. 75 Ω Coaxial Cable
One of the popular and frequently used coaxial cables is the 75 Ω Cable. The cable that you use for your Cable TV is typically a 75 Ω Coaxial Cable. Apart from cable TV, the 75 Ω Coaxial Cable is also used in RF audio and video transmission.
Based on Design and Construction
The design and construction of the coaxial cable is also significant factor. Here are 5 types of Coaxial Cables with different kinds of construction.
1. Flexible Coaxial Cable
If you are looking for a coaxial cable either online or in brick-and-mortar stores, chances are you will find one of the Flexible Coaxial Cable. It is one of the most common types of Coaxial Cables out there. You can easily identify a flexible coaxial cable by looking at its braided cable design. The braided external conductor makes the coaxial cable more flexible. But sadly, the lack of a proper outer layer means this type of cable is susceptible to signal leakage as there is no shielding.
2. Semirigid Coaxial Cable
If shielding and preventing signal leakage is your priority than flexibility, then the Semirigid Coaxial Cable is an ideal choice. As the name suggests, the construction of this type of coaxial cable is rigid and durable, similar to pipes. There is an exterior metallic layer that acts as a secondary conductor. In addition, the metal layers also help in maintaining a uniform impedance throughout the length of the cable. But the rigid structure of the cable means you won’t find it that flexible.
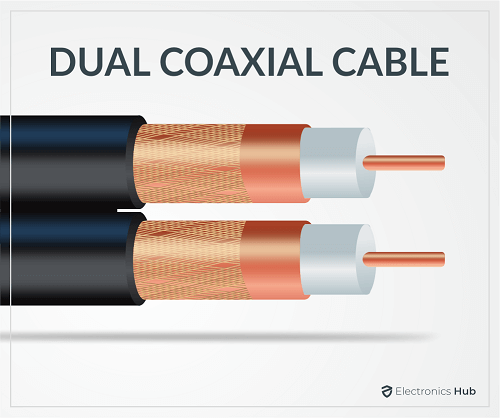
3. Dual Coaxial Cable
This is a unique type of cable that consists of two individual coaxial cables wrapped in a single outer plastic sheathing.
4. Twinaxial Coaxial Cable
No to be confused with Dial Coaxial Cable, in a Twinaxial Coaxial Cable, you get two insulated copper conductor wires that are wrapped using a single external shield. The two copper conductors run parallel to each other. These types of cables are very common in high-speed networking to transmit high-bandwidth data.
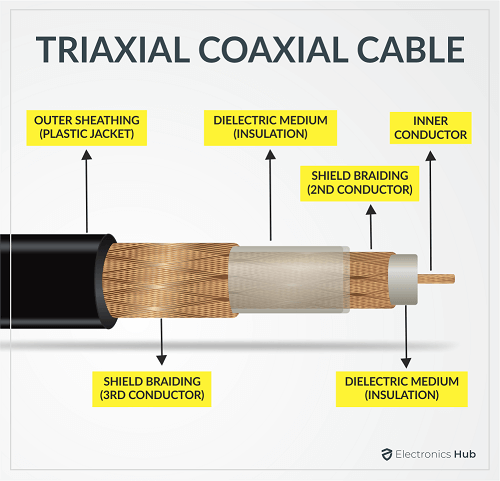
5. Triaxial Coaxial Cable
Also known as Triax Cable, the Triaxial Coaxial Cable has two copper conductors that are separated by a dielectric insulator. One conductor carries the main signal while the other conductor acts as a ground or return path. Due to the design and construction of Triaxial Coaxial Cables, you get better shielding, signal-to-noise ratio, and very minimum interference. Triaxial Cables can carry high-bandwidth data with very less signal leakage. Based on RG (Radio Guide) Standard Radio Guide or RG is an old military designation for coaxial cables. They do not have significant specifications or performance numbers. For instance, the most common coaxial cable RG-6 means that the main copper conductor is an 18 AWG wire. Nowadays, the “RG” designator mainly refers to the connector type. We will see different types of Coaxial Cable Connectors in the next section. But for now, let us take a look at some common RG Coaxial Cables.
Different Kinds of Connectors For Coaxial Cables
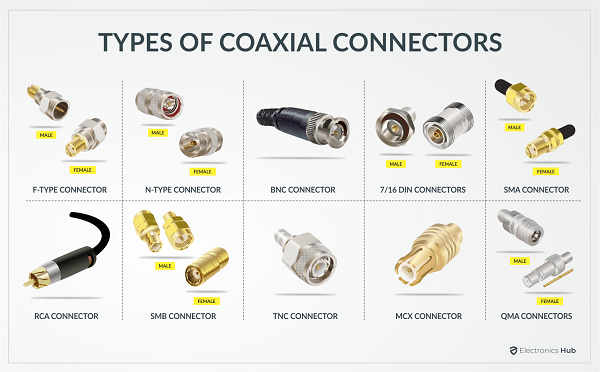
Connectors are as important as the cable as they help you terminate the cables and allow you to connect the cables to different devices or appliances. Let us now see some common, popular, and even not-so-popular connectors that we use with coaxial cables.
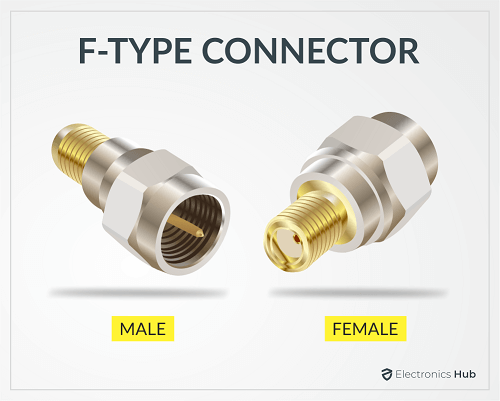
1. F-Type Connector
One of the most popular Coaxial Cable Connectors is the F-Type Connector. If you have a cable TV connection, then chances are you use this type of connector to connect the cable to your set-top box or receiver. The combination of RG-6 Coaxial Cable with an F-Type Connector is very common in the cable tv industry. As a result, they are available everywhere and are inexpensive as well. Coming to the performance side of things, Coaxial Cables with F-Type Connector usually can handle frequencies up to 1 GHz. You can get F-Type Connectors in both 50 Ω and 75 Ω impedances.
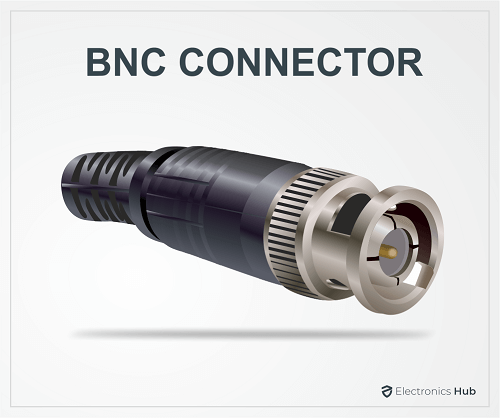
2. BNC Connector
Another popular Coaxial Cable Connector is the BNC Connector. The majority of the commercial applications of coaxial cable such as RF Video Transmission (CCTV), Test Equipment, Scientific Apparatus, RF Devices, Amateur Radio Equipment, etc. use BNC Connectors. As their applications are with high-end RF equipment, the BNC Connectors have a higher frequency rating of 2 GHz.
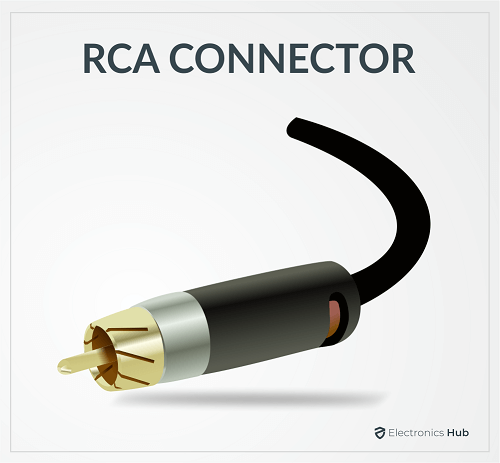
3. RCA Connector
The RCA Connector is one of the oldest connectors. All old-school analog audio and video such as Composite Video, Stereo Audio, Component video, etc. used the RCA Connector. When we talk about Coaxial Speaker Cable in the later sections, we will see that the RCA Connector is the preferred choice for the Digital Audio Cable using Coaxial and S/PDIF. Modern speakers, subwoofers, and other home theatre devices still use RCA Connectors. They can carry signals with frequencies up to 100 MHz.
4. N-Type Connector
It is one of the earliest Microwave RF Connectors that can work at frequencies up to 11 GHz but some versions can push up to 18 GHz. Due to its rugged and weather-proof design, the N-Type connectors are very common in several low-frequency Microwave Applications. Spectrum Analyzers, Antennas, etc. use N-Type connectors with coaxial cables as their input.
5. SMA Connector
Similar to N-Type connectors, the SMA Connectors are also useful in Microwave frequencies in the range of DC to 12 GHz. Modern SMA Connectors can handle even higher frequencies up to 26.5 GHz. Some applications of SMA Connectors are Microwave Frequency Equipment, Hand-held and telephone antennas, Wi-Fi Antennas, SDR (Software Defined Radio) Antennas, etc.
6. SMB Connector
If you are looking for a much smaller connector than the SMA Connector, then the SMB Connector is a good choice. But the operating frequency falls to 4 GHz.
7. TNC Connector
The TNC is a threaded version of the BNC Connector. The operational frequency can be as high as 11 GHz. So, the TNC Connector is suitable for lower microwave frequency applications.
8. MCX Connector
Micro Coaxial Connector or simply MCX Connector is a popular coaxial cable connector in Europe. The passband frequency of the MCX Connector is up to 6 GHz. Software Defined Radios (SDR), Software Oscilloscope, Signal Generators, and other inexpensive RF Equipment use the MCX or its smaller version, the MMCX Connector.
9. QMA Connector
The QMA Connector is a quick connect replacement for the SMA Connector. However, their frequency of operation is only up to 6 GHz. Mobile Phone Base Station Antennas, Defense, and Military RF Communication devices use the QMA Connector.
10. 7/16 DIN Connector
Another threaded RF Connector is the 7/16 DIN Connector. High-power RF Connections in cell phone antenna networks use this type of connector. If you take the cross-section of all these different cylindrical layers, they have the same axis. Hence the name Coaxial Cable.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Coaxial Cables
- One of the oldest and still using Cable types
- Low-price, wide availability, and easy to install (for short distances)
- Very durable and offers reliable performance for short and long distance
- Suitable for high-frequency applications, 50 MHz or more
- Can support very wide bandwidth RF Signal Transmission
- Popular Choice for low to medium RF Communication
- Even lower microwave frequency applications use coaxial cables
- Very less loss of signal
- Less chance of EMI or Radio Interference
- Tough and rugged. Suitable for harsh and rough environments – Bulky design and construction – Signal loss in case of long-distance communication – Chance of signal leakage at the connector – Longer cables are difficult to install and have higher capacitances
Applications Of Coaxial Cables
As we have already seen, the main application of Coaxial Cable is Cable TV Transmission. The cable from your cable TV company is a coaxial cable. They are also popular for cable broadband internet connections. Coming to specialty applications, coaxial cables are useful in several RF Communication Systems. CCTVs, RF Video and Audio, Cable between the Satellite Dish and its receiver, etc. all use coaxial cables. Apart from these, several medical appliances use RF Coaxial Cables for power and data transmission. Cellular Base Stations, Amateur Radio Systems, and Microwave Frequency applications use coaxial cables with different types of connectors.
What Is Coaxial Speaker Cable?
After all the discussion about Coaxial Cables, we haven’t really touched their audio capabilities. So, the important question is, can we use Coaxial Cable as a Speaker Cable? If both the source such as the TV or AV Receiver and the Speaker support Digital Audio over S/PDIF Coaxial, then yes, we can use coaxial cables as speaker cables. The Sony Phillips Digital Interface has two audio interfaces. One uses the traditional RCA Connector with Coaxial Cable and the other uses TOSLINK Connector with Optical Fiber Cable. Both these interfaces can digital audio. If you want uncompressed PCM audio from Digital Coaxial Cables or Optical Fiber TOSLINK Cables, then you will be limited to two channels. But they can carry Dolby Digital or DTS 5.1 compressed audio using a single Coaxial Cable or TOSLINK Cable. Advanced formats such as Dolby Digital Plus, DTS:X, Dolby Atmos, etc. are not supported. Digital Coaxial Speaker Cable uses an AWG 18 core RG-6/U style Coaxial Cable with RCA Connector. The main difference between the old-school analog RCA Cable and the Digital Coaxial Audio Cable with RCA Connector is the characteristic impedance. Analog RCA Cables have a 50 Ω Impedance while Digital Coaxial Audio Cables have a 75 Ω Impedance.
Can We Use Regular Coaxial Cable as Speaker Cable?
Most common coaxial cables in the market with F-Type Connectors and RG-6/U have an impedance of 75 Ω. Even if you replace the F-Type Connector with an RCA Connector to use it with speakers and subwoofers, the impedance mismatch will be a significant problem. So, use only Digital Coaxial Speaker Cable with speakers and sources that support S/PDIF Digital Audio over coaxial.
Conclusion
Coaxial Cable is one of the oldest and yet still-in-use types of transmission medium. While you may have used a coaxial cable for cable TV or cable internet, many people often wonder about its usage as speaker cables. In this guide, we saw the basics of Coaxial Cable. We saw its types, connectors, pros, and cons. After that, we looked at Digital Coaxial Speaker Cable that uses an RCA Connector Coaxial Cable to transmit S/PDIF Digital Audio. Comment * Name * Email * Website
Δ








![]()