A Brief Note on ESP32 ADC Peripheral
The ESP32 SoC consists of two Successive Approximation Register (SAR) type Analog to Digital Converters (ADC). Together, the two SAR ADCs i.e., ADC1 and ADC2 in ESP32 consists of 18 channels. ADC1 consists of 8 channels and ADC2 consists of 10 channels. ADC in ESP32 have a maximum resolution of ADC of 12-bits and yes, the resolution of ADC is configurable with possible values include 9-bit, 10-bit, 11-bit and 12-bit. Usually, the resolution is set to 12-bit, if not changed. So, by default, the output of the ESP32 ADC will be a value in the range of 0 and 4095 (as the default resolution is 12-bit, the output digital values can have 212 = 4096 values). Also, the ADC input voltage limit is 3.3V i.e., ESP32 ADC can measure analog voltage in the range of 0V to 3.3V.
ADC Pins of ESP32
Unlike some of the digital peripherals (PWM, software SPI and I2C), the ADC pins are fixed i.e., you have to use the predefined GPIO Pins which have ADC functionality and you cannot configure it in software. However, there are some limitations you have to know of. Even though ESP32 has 18 channels ADC, all the ADC pins are not available for the user. Of the 8 ADC1 channels, only 6 are available (ACD1_CH0 and ACD1_CH3 to ACD1_CH7) while ADC1_CH1 and ADC1_CH2 are not available (even the pins are not exposed in the ESP32 Development Board). Coming to ADC2, it is somewhat complicated. When you are using the Wi-Fi of ESP32, the Wi-Fi Driver uses the ADC2 Peripheral. So, you can use ADC2 only if the Wi-Fi driver is not started. Even when you are using ADC2 (assuming Wi-Fi is not used), all the pins are not readily available as some of the pins associated with ADC2 are used for other important purpose (Boot Strapping). The following table shows the ADC Channels, Arduino style names (A0, A1, etc.), GPIO Pins and any important points to remember. By taking account of all the information mentioned above, it is a safe bet that the 6 available ADC1 pins (ACD1_CH0 and ACD1_CH3 to ACD1_CH7) can be used without any ambiguity. ADC1_CH0 and ADC1_CH3 are also associated with Hall Effect Sensor. Other ESP32 Development Boards may have their own restrictions. So, definitely check for the datasheet and schematic and check if a particular ADC pin is free to use or not.
ADC Functions
There are nine function exposed by the ADC driver. They are:
analogRead(pin): Get the ADC Value for the specified pin. analogReadResolution(bits): Set the resolution of output of analogRead. Default is 12-bit but possible values are 9 to 12. analogSetWidth(bits): Sets the sample bits and read resolution. Default is 12-bit but range is 9 to 12. analogSetClockDiv(clockDiv): Set the divider for the ADC clock. analogSetAttenuation(attenuation): Set the attenuation for all channels. Default is 11db but possible values are 0db, 2_5db, 6db, and 11db. analogSetPinAttenuation(pin, attenuation): Set the attenuation for a particular pin. adcAttachPin(pin): Attach pin to ADC (done automatically in analogRead). analogSetVRefPin(pin): Set pin to use for ADC calibration if ESP32 is not already calibrated. Possible pins are 25, 26 or 27. analogReadMilliVolts(pin): Get millivolts value for pin.
Measure Analog Voltage
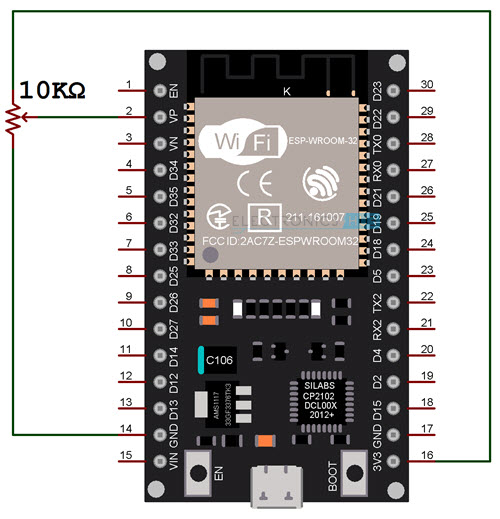
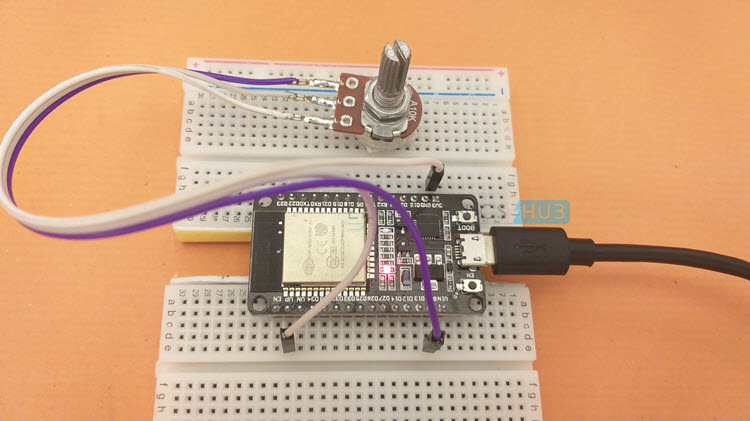
With the theory, pin information and library functions laid out, we can now start to develop circuits to actually use the ADC Peripheral of ESP32. For the first project, let us see how to configure the ADC channel of ESP32 and measure an analog voltage applied to one of the ADC Pins.[ESP32 Projects for Beginners] The simplest way to provide variable analog voltage is with the help of a Potentiometer. Connect the ends of POT to 3.3V and GND of ESP32 Development Board and connect the Wiper to any of the ADC Pin. To keep things simple, I used the ADC1_CH0 i.e., GPIO 36 (A0) as the ADC Pin.
Components Required
ESP32 DevKit Development Board 10 KΩ Potentiometer Breadboard Connecting Wires 5mm LED 220Ω Resistor
Circuit Diagram
The following image shows the circuit diagram for measuring analog voltage using ADC of ESP32.
Code
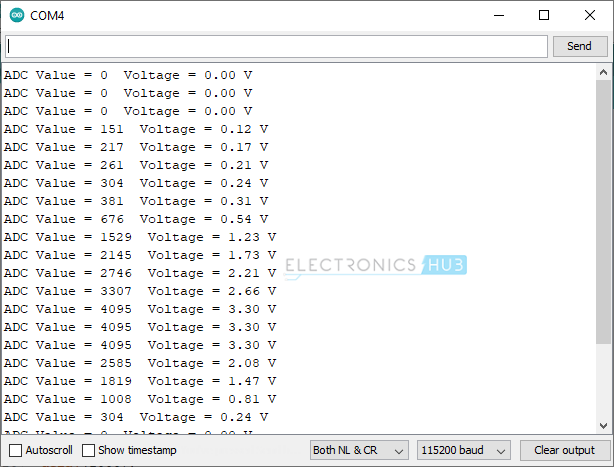
The code is very straight forward if you ever worked with ADC of Arduino or ESP8266. Read the ADC value of the ADC Pin (A0 in this case) using ‘analogRead’ function, convert the digital value into voltage using a small calculation and display the result on Serial Monitor.
The output of the Serial Monitor looks something like this:
LED PWM using ESP32 ADC
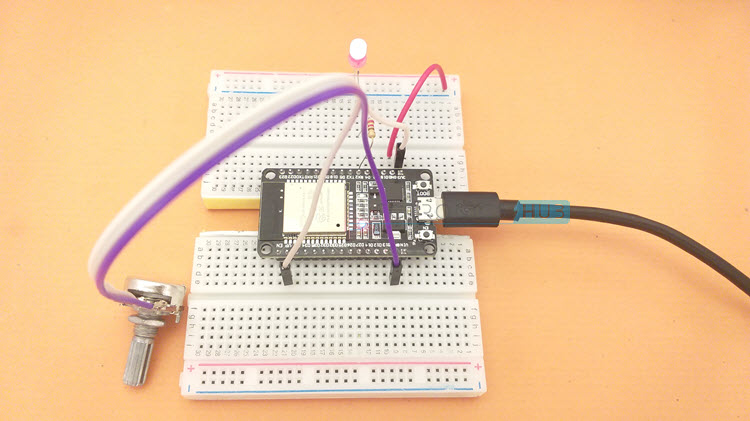
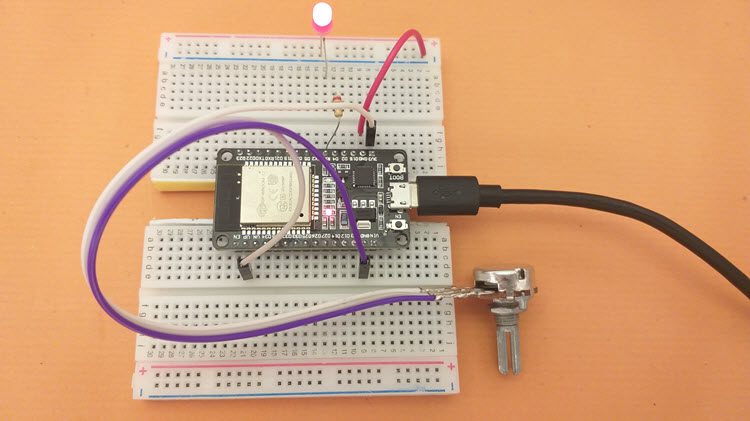
I made a dedicated tutorial on the working of LEDC PWM in ESP32. Read that tutorial for in-depth understanding of PWM in ESP32. We can set the duty cycle of the PWM output of ESP32 using ADC. The ADC Pin is the same as earlier i.e. A0 (ADC1_CH0 – GPIO 36) and the PWM Pin is GPIO 16. I connected a 5mm Red LED to this pin using a 220Ω current limiting resistor.
Circuit Diagram
The following image shows the circuit diagram for manually configuring the duty cycle of PWM using ADC of ESP32 and thus adjusting the brightness of an LED.
Code
Conclusion
A complete tutorial on using ADC Module in ESP32. You learned about the ESP32 ADC Peripheral, its associated pins, what ADC pins are safe to use, how to measure analog voltage using ADC in ESP32 and also how to manually adjust the brightness of an LED using ADC and PWM in ESP32. Comment * Name * Email * Website
Δ






![]()