Ethernet cables are fairly long and therefore you won’t have any issues with data loss. They are compatible with almost any kind of hardware as well. Ethernet cables come in different sizes and with different speeds. In this article, we will be looking at the different variants of ethernet cables in a detailed manner. Read on to find out more.
Types of Ethernet Cables
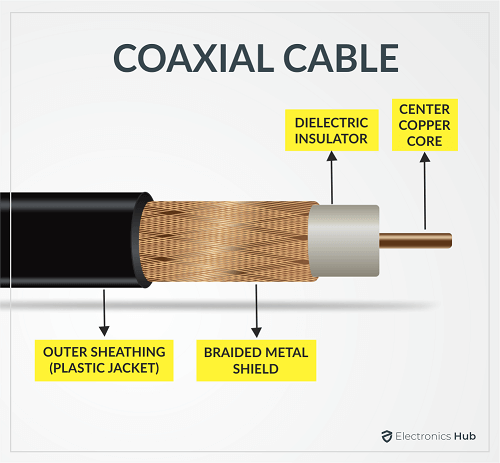
Coaxial Cabling
Coaxial cables feature a conductor on the inside which is surrounded by a layer of insulation. This layer is surrounded by another conducting shield. This cable is not affected by outside interference. These cables have a maximum transfer rate of around 10 Mbps. Nowadays, they have been replaced by twisted cabling.
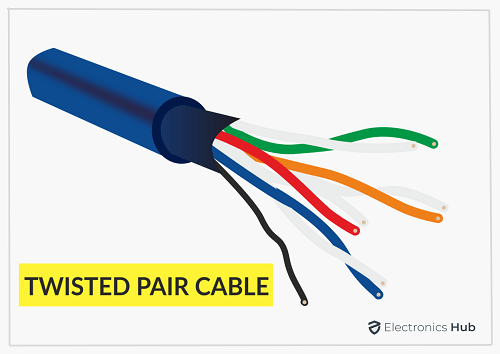
Twisted-pair Cabling
This type of cable has 4 pairs of wires. The wires are twisted together to keep outside interference to a minimum. This type of wiring can be found in LANs. There are 2 types of twisted pair cables-UTP and STP. The key difference is the fact that the STP has an extra layer of insulation.
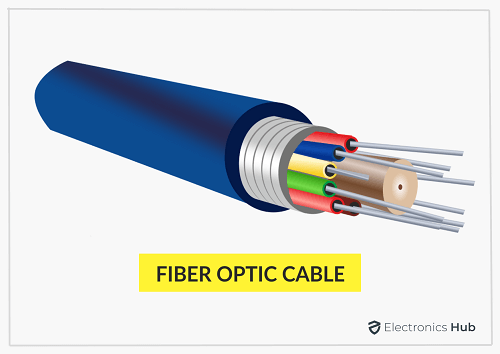
Fiber-optic Cabling
These cables make use of optic fibers to transmit data. The data transfer is in the form of light. Within the cable, there are glass strands that are covered by cladding. It is very fast but quite expensive as well. Moreover, the cables are practically immune to electromagnetic interference. Optical fibers are of two types-Single mode fiber and Multi-Mode Fiber. The difference lies in the number of light rays used to transmit data.
Categories for Ethernet cables
Cat-1 This was once used in telephone systems and had two copper wires twisted around each other. It was meant for analog communication. However, it is not recognized by the EIA. Cat-2 It allows for both voice and data communication. It was mainly used in the IBM token ring networks and had a data transmission rate of 4 Mbps. Cat-3 Cat 3 came out in the 1990s and had 4 twisted pairs of wires. It is capable of working with networks having frequencies of up to 16 MHz. It was mainly used with 10 Mbps ethernet networks. However, it has been replaced by Cat 5. Cat-4 Cat 4 had a maximum data transfer rate of 16 Mbps and was used in networks with a frequency of 16 MHz. Cat-5 Cat 5 arrived in the mid-1990s and has a maximum transfer speed of 100 Mbps. It can transfer data up to a distance of 100 meters. It was the standard ethernet for ethernet cables for a long time. However, currently, it’s obsolete. Cat-5e Cat 5 was not recognized by the EIA but the 5e was recognized. It has sped up to 125 Mbps and higher frequency specifications as well. Physically, it is quite similar to the Cat 5. Cat-6 When compared to the Cat 5, cat 6 offers much higher bandwidth and data transfer rates. It can achieve speeds up to 1 Gbps over a distance of 100m. For shorter distances, the speed can be around 10Gbps. Cat6 has a separator called the Spline to minimize crosstalk and reduce electromagnetic interference. It is also backward compatible with the Cat 5 and 5e. Cat-6a Cat 6a is an augmented version of the Cat 6 and can support higher speeds and bandwidth. Crosstalk is absent but the cable is not as flexible as the Cat 6. Cat-7 Cat 7 has similar specifications to the Cat 6a and has a robust shielding and allows for a maximum data transfer rate of around 10 Gbps and a bandwidth of 600 MHz. Cat-8 Cat 8 cables are more expensive than Ca7 or the Cat 6a but are much more capable. They support a data speed of 40 Gbps and come with a maximum bandwidth of 2000 MHz.
Ethernet Cable Performance Table
Ethernet Cable Connectors
The RJ45 is the most commonly used connector for the ethernet cable. It is used in all ethernet cables from Cat 3 to Cat 6. Cat 7 makes use of a specialized version of this connector called the GG45. It is backward compatible with the RJ45. This connector has a total of 8 pins that are spaced 1 mm apart and the wires are cramped to offer a solid connection.
Conclusion
We hope you enjoyed this guide on Ethernet cables. There are different categories of Ethernet cables and it is important that you learn about them before making a purchase. For any queries regarding the content, do write to us. Comment * Name * Email * Website
Δ





![]()